Overview of Reflective Ecore Model Diagram Editor
Introduction
Reflective Ecore Model Diagram Editor dynamically loads a meta-model, and
provides a diagram editor for editing its instance. In a general case, from a
meta-model you generate model, edit, and diagram code by using EMF and GMF. On
the other hand, Reflective Ecore Model Diagram Editor provides a diagram editor
directly from a meta-model by using EMF reflective APIs.
It's assumed that readers of this document are familiar with EMF and GMF.
Dynamic loading of meta-model
In the case of .xsd file as a meta-model, the editor converts it into a dynamic Ecore
model by using XSDEcoreBuilder. The editor saves the location of the given
meta-model file as "xsi:schemaLocation" attribute in .xmi_diagram/.xml_diagram file. The
attribute enables that the editor finds the meta-model and converts it when
opening again.
Nodes on the palette
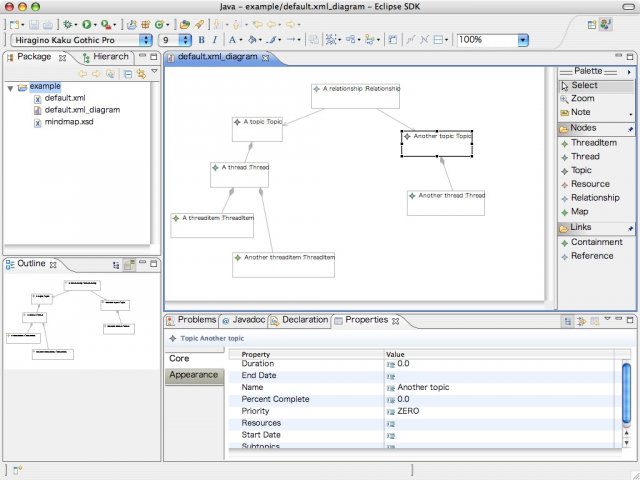
Once the editor loads your meta-model, it places every non-abstract
EClass in the meta-model on the palette. For example, if the editor loads
mindmap.xsd (its
class diagram
) as a meta-model, complex types in the xsd are converted into EClasses
and placed as "nodes" on the palette, i.e., ThreadItem, Thread, Topic,
Resource, and Relationship are put on the palette. In this example, however, Map class is not put on the palette
because it is the root class corresponding to the diagram canvas and it is not instantiated as a child
for any classes.
Note that association classes such as Relationship are also placed as "nodes" on
the palette instead of "links" because the editor cannot recognize as a link.
Links on the palette
Two kinds of link creation tool are supported: "Containment" and "Reference".
"Containment" creates EReference with containment="true" and resolveProxy="false", whereas "Reference"
creates EReference with containment="false". If no EReference with
containment="false" exists in the meta-model, this creation tool does not appear
on the palette.
Which EClass is the diagram root element?
GMF requires an EClass which corresponds to the diagram root element. In
Reflective Ecore Model Diagram Editor, the root element has to be determined
dynamically. If .xsd files is given as a meta-model, the type of the root
element defined in the XSD is chosen as the diagram root element. In the case of
.ecore file, the creation wizard asks after loading the dynamic Ecore.
Editing model instance
You can create an instance by using node creation tools on the palette. Click
one of the nodes on the palette, then click again on the canvas. If the node can
be contained by the diagram root element, the node is added/set to the
appropriate feature of the root element EClass. If not, the node is treated as a
phantom node by the editor. Phantom nodes can be contained by other nodes by
connecting links using "Containment" link creation tool on the palette. Of
course, the editor does not allow to make a connection which is not defined in
the meta-model.
Label on a node
Once you put a node on the canvas, you might be able to edit its label. The
label corresponds to a String attribute of its underlying semantic model. The
attribute is selected according to the same algorithm as EMF's
ReflectiveItemProvider.
Editing other attributes of a node
You can edit other attributes of a node on the Properties View.
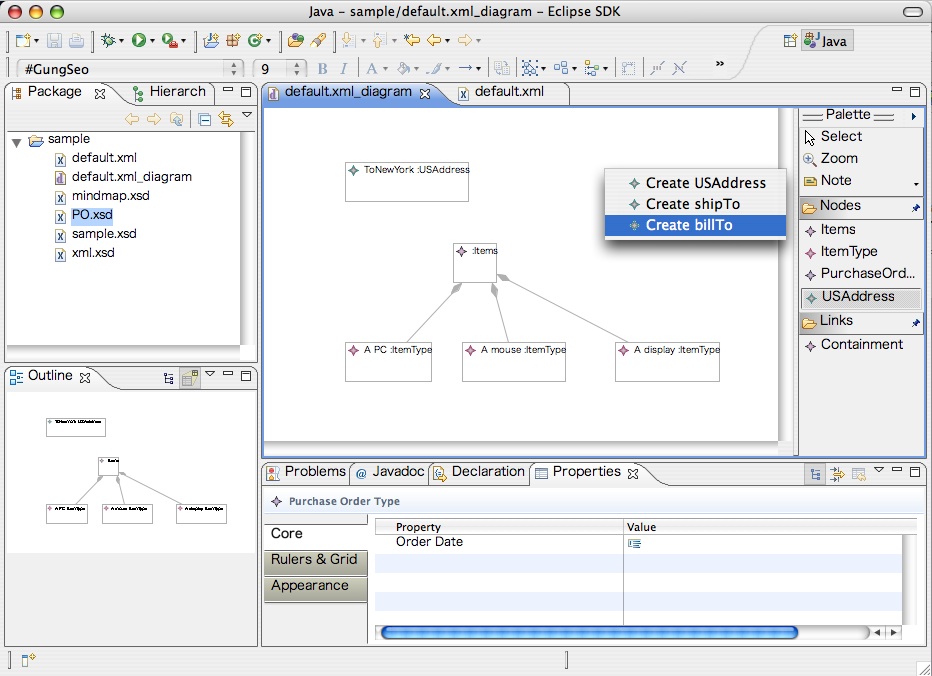
When you are going to put a new element from the palette, or connect elements
as Reference or Containment, there may be multiple structural features to add
the element. In this case, a popup menu appears to select which features you are
adding the element to, as shown in the following screen-shot.